Overview
General architecture
Stellio is composed of 2 business services:
- One service (called
search-servicein the source) is in charge of handling the requests for the Core and Temporal APIs. It is backed by a PostgreSQL database, extended with the TimescaleDB and PostGIS extensions - One service (called
subscription-servicein the source) is in charge of handling the requests for the Subscription API. It is backed by a PostgreSQL database, extended with the PostGIS extension
It is completed with:
- An API Gateway component, based on Spring Cloud Gateway, that simply forwards the incoming requests to one of the downstream services, based on the request path
- A Kafka streaming engine that decouples communication inside the broker (and allows plugging other services seamlessly). It is described in more details in the internal event model page.
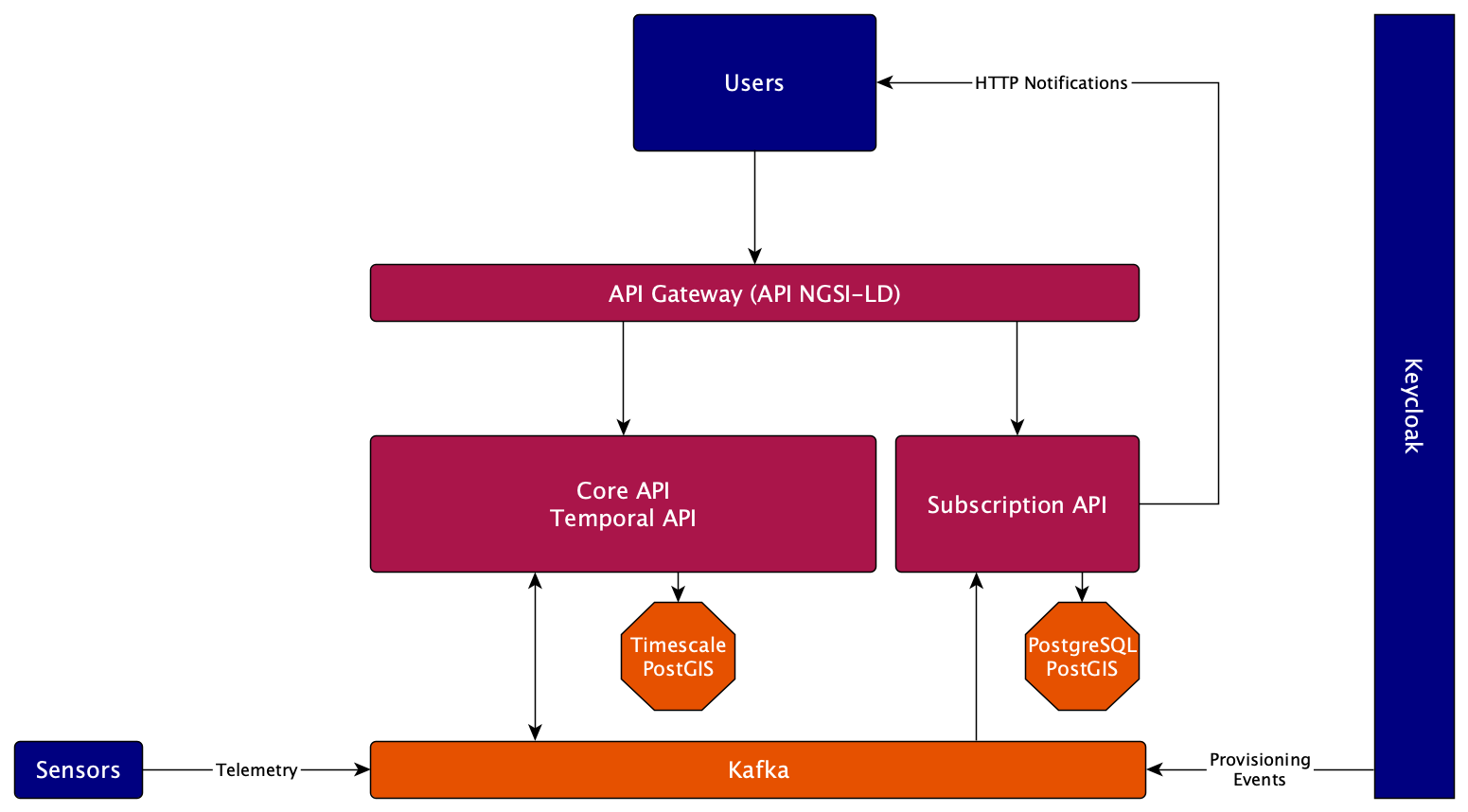
The services are based on the Spring Boot framework, developed in Kotlin, and built with Gradle.
Quick start
A quick way to start using Stellio is to use the provided docker-compose.yml file in the root directory
(feel free to change the default passwords defined in the .env file):
docker-compose up -d && docker-compose logs -f
It will start all the services composing the Stellio context broker platform and expose them on the following ports:
- API Gateway: 8080
- Search service: 8083
- Subscription service: 8084
Please note that the environment and scripts are validated on recent Ubuntu versions and MacOS. Some errors may occur on other platforms.
Docker images are available on Docker Hub.
Development
Developing on a service
Requirements:
- Java 17 (we recommend using sdkman! to install and manage versions of the JDK)
To develop on a specific service, you can use the provided docker-compose.yml file inside each service's directory, for
instance:
cd search-service docker-compose up -d && docker-compose logs -f
Then, from the root directory, launch the service:
./gradlew search-service:bootRun
Running the tests
Each service has a suite of unit and integration tests. You can run them without manually launching any external component, thanks to Spring Boot embedded test support and to the great TestContainers library.
For instance, you can launch the test suite for entity service with the following command:
./gradlew search-service:test
Building the project
To build all the services, you can just launch:
./gradlew build
It will compile the source code, check the code formatting (thanks to ktLint) and run the test suite for all the services.
For each service, a self executable jar is produced in the build/libs directory of the service.
If you want to build only one of the services, you can launch:
./gradlew search-service:build
Working locally with Docker images
To work locally with a Docker image of a service without publishing it to Docker Hub, you can follow the below instructions:
- Build a tar image:
./gradlew search-service:jibBuildTar
- Load the tar image into Docker:
docker load --input search-service/build/jib-image.tar
- Run the image:
docker run stellio/stellio-search-service:latest-dev
Usage
To start using Stellio, you can follow the API quick guide.
As the development environment does not make use of the authentication setup, you can ignore related information in the API quick guide.